Carbohydrates
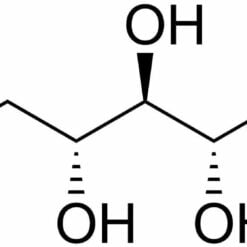
Carbohydrates, often called sugars, are one of the major biochemical groups essential for life. They are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, typically in a 1:2:1 ratio. Their primary functions in living organisms are to provide energy and to play a structural role in cells and tissues.
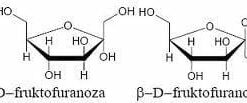
Carbohydrates are divided into simple sugars, known as monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, which are the basic energy units utilized by cells. Oligosaccharides, consisting of a few sugar units, and polysaccharides, which are long chains of monosaccharides, perform both energy and structural functions.
The use of carbohydrates in the food industry
In the food industry, carbohydrates are used not only for their energy value but also because of their texturing and flavoring properties. They serve as sweeteners, stabilizers, emulsifiers, and gelling agents, making them ubiquitous in many food products. In medicine, carbohydrates are used in the production of medicines and as carriers for many pharmaceutical forms, enabling effective delivery of active ingredients in therapeutic treatments.
The importance of carbohydrates in biology, medicine, and technology is immense and continues to grow as more applications and mechanisms of their action at the molecular level are discovered.
Additives for Dietary Supplements
Raw Materials for Production
Raw Materials for Production