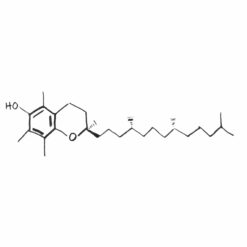
Properties of vitamin B1
Thiamine plays a key role in the conversion of carbohydrates into energy, being essential for the proper functioning of cellular mitochondria. It is also important for nervous system health, as it participates in nerve conduction, supporting the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system. Thiamine deficiencies can lead to neuropathy and impaired concentration. In the context of the cardiovascular system, thiamine helps maintain normal heart rhythm and supports cardiac muscle function, and a deficiency can result in muscle weakness and circulation problems. Thiamine is also used in the treatment of beri-beri disease, the result of its deficiency, which manifests itself in weakness, weight loss and heart disorders.
Application
It is also widely used in supplementation and pharmacy, as an additive in vitamin preparations, dietary supplements and functional food products, including sports nutrition. Thiamine plays a key role in treating B vitamin deficiencies, supporting the body’s overall health.