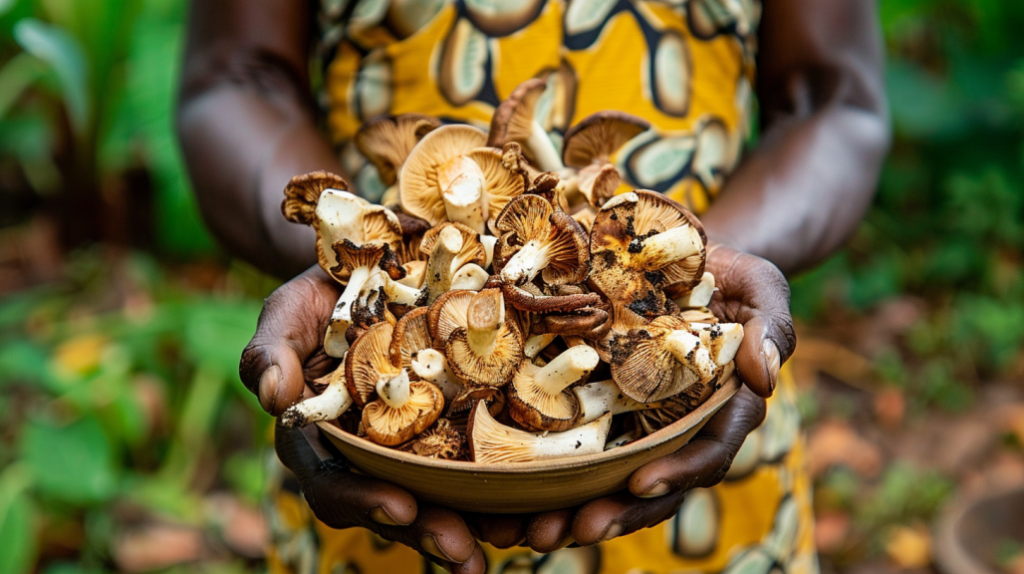
The natural health and beauty care industry, on the other hand, is constantly searching for new and highly efficient raw materials. Unlike most other natural resources, African mushrooms are the rising star in the skincare and nutrition fields. They are a promising bridge between Africans who have used wisdom for many years and medical scientists. This article examines the dynamics of food production in urban farming systems. Firstly, the nutritional benefits are brought to the forefront. This is then reverberated through skincare applications, scientific culture backing, and the impact on the local community.
Nutritional Powerhouses Unearthed
African mushrooms, which are the most sellable ones, include the shiitake and yam-like termitomyces species. Among the less prepared ones are reishi, oyster mushrooms, and others. The termitomyces species has better nutritional potential than some common species, thus making them an excellent choice of leafy greens. You’ll be glad to hear that these fungi are rich in protein and also supply all the essential amino acids the body needs: vitamins (B, D, and E), minerals (selenium, potassium, and iron), and fibers. They thereby got themselves the status of a superfood, an essential advantage in regions where malnutrition is prominent.
The calorie- and nutrient-rich contexts of minerals, vitamins, and fiber are naturally low in calories, which help to maintain body weight and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. Of note, the beta-glucans in these species of mushrooms are particularly useful in regulating the immune system, setting the foundation for their consideration as a dietary supplement for health maintenance and prevention of diseases.
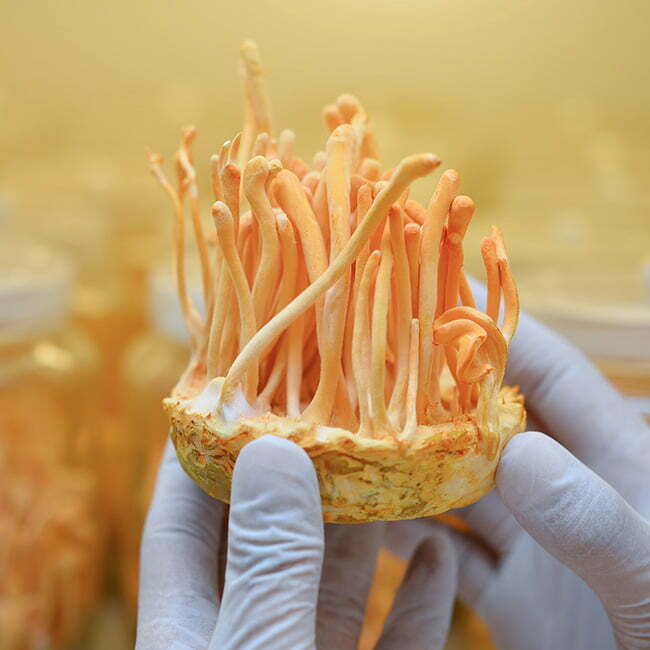
Mushroom extracts
We sell standardized mushroom extracts. Our mushrooms come from Chinese farms where they are grown using natural methods. Most of them are grown on tree bark.
The mushrooms are extracted with hot water, thanks to which their most important bio-components, such as beta-glucans and other polysaccharides, remain intact.
A Revelation in Skincare
Besides feeding us nutritiously, what the wild African fungi are doing now is being incorporated into skincare products. Rich in antioxidants, they combine free radicals; in this way, decreasing oxidative stress and aging are avoided. I want to say that some fungi, namely mushrooms, contain kojic acid, which is regarded as a natural skin bleach. It has the potential to address hyperpigmentation and bring about skin tone evenness without any adverse effects associated with chemical agents.
Interestingly, the inflammation-fighting qualities of mushrooms help deal with skin problems like acne, caviar, and dermatitis. Lastly, the moisture-binding aspect is another great thing about mushrooms, as they have polysaccharides, making the skin moist and healthy, resulting in a plump and youthful appearance. These benefits have the advantage of being endorsed by scientific studies, which are thus incorporated into specialized cosmetics such as serums, creams, masks, and cleansers manufactured by mushroom extract producers.
Scientific Backing and Potential
The African mushrooms are receiving a great deal of interest from researchers, and scientific discoveries are continuing to be made. Scientists have proved that some organisms have anticancer cell potential; from one standpoint, they induce apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells but not in mortal cells. Thus, they target cancer cells specifically. On the other hand, scientists are studying the neuroprotective effects of mushrooms to possibly use the ganglia for the prevention of Alzheimer’s or the management of Parkinson’s disease.
On the other hand, scientific research on African fungi is quite a new field, and most of the knowledge on it is still with the traditional healers’ practice with anecdotes. This absence of information is an inspiring chance for conducting further studies with excellent prospects to develop compounds and benefits that can set the pace in the health care, wellness, and even the pharmaceutical industry.
Empowering Society and Inspiring Sustainability
The growth of African mushroom attraction, in addition, submerges with considerable consequences for the locals and sustainability. Various perspectives from different people can make the class more vibrant, showing a diversity of skills and backgrounds in the classroom. Compared to traditional cash crops, the advantage of mushroom cultivation becomes evident. It doesn’t require much investment, and you can grow it on a small scale with various substrates, including agricultural wastes. This way, waste reducing also a part of circular economy principles.
Besides, advertising indigenous mushroom species emphasizes the significance of biodiversity and the conservation of historical know-how. This method ensures a shift from the mono-cultural farming approach to multi-cultural crop production, thus maintaining the local agro-ecosystem resiliency by strengthening the livelihoods of farmers and gatherers. Sustainable harvest and mushroom cultivation can help demonstrate a successful model, similar to many other natural resource-based industries, which follow nature preservation as the essential requirement.
Conclusion
Through African mushrooms, it is evident that the region has enough food to feed families and more nutritional and aesthetic benefits. Their stunning food courses and tutorials on skin benefits, which incorporate traditional knowledge and scientific research, open the way to alternative notions of health and beauty. These natural resources not only manage this sustainability but also support our communities as serious empowerers and refugees and biodiversity. As the global community will still have to find regenerative and nature-based therapies that are practical and sustainable, African mushrooms can be one of the options with qualities that speak of all these concepts. The trip into the fungi’s kingdom is just a taste. More is coming, with all the hope that health, beauty, and sustainable nature can exist in harmony.



