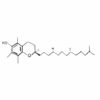
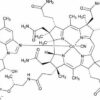
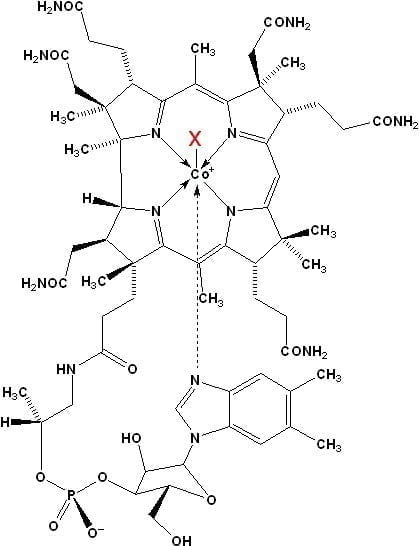
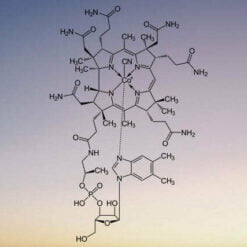
Main properties and functions of methylcobalamin:
Vitamin B12, in the form of methylcobalamin, supports hematopoietic functions, is responsible for the production of erythrocytes (red blood cells) and supports the processes of DNA and RNA synthesis. As a result, it prevents megaloblastic anemia and helps avoid symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, concentration problems and pale skin. Vitamin B12 also affects the function of white blood cells, supporting immunity and the body’s ability to fight infection. B12 is also essential for the synthesis of myelin, the protective covering of neurons, helping to improve nerve conduction. It has a positive effect on cognitive function, improving memory and concentration, and reduces the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and depression. Vitamin B12 helps reduce fatigue and improves energy metabolism. What’s more, methylcobalamin helps lower levels of homocysteine, an amino acid linked to the risk of cardiovascular disease. By regulating homocysteine levels, it reduces the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attacks and strokes. Natural sources of vitamin B12 are primarily animal products such as meat, fish, eggs and dairy, so supplementation is crucial for those on a plant-based diet. Supplements with methylcobalamin are also recommended for the elderly, as their ability to absorb this vitamin decreases with age. Recommended dosage and safety – Methylcobalamin supplementation is worth adjusting to individual needs, usually in doses of 500 to 1,000 µg per day, under the supervision of a doctor or nutritionist. Vitamin B12 is safe and does not accumulate in the body, as excess is excreted in the urine.