Chitosan is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry and medicine for its properties facilitating wound healing and reduction of bleeding, as well as in dietary supplements designed to aid weight loss. What is chitosan and what makes it distinct from other compounds?
Chitosan – what is it?
Chitosan is a chain polyaminosaccharide formed by partial deacetylation of chitin. It is composed of a deacetylated unit (β-(1,4)-d-glucosamine) and an acetylated unit (N-acetyl-d-glucosamine). Chitosan is obtained from the hard exoskeleton of crustaceans such as crabs, lobsters and shrimp.
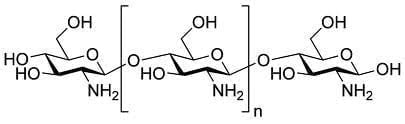
Chitosan
Chitosan is a derivative of chitin. It’s widely applied in medicine since it’ s great for stopping hemorrhages and dressing wounds.
Chitosan is also a well-known dietary supplement that helps to lose weight. It’s an organic compound belonging to the group of polysaccharides. The supplement isn’t digested by the human body.
Importantly, it is not only natural, but also biocompatible, biodegradable and non-toxic, while being relatively easy to process and create various chemically and enzymatically modifiable forms. These properties allow chitosan to be used in medicine as a biomaterial – in the form of sutures, artificial skins as well as bandages and dressings used in wound treatment. In addition, due to its ability to bind to cholesterol, fats, proteins and metal ions, it also finds use when administered orally.
Plant-based chitosan
Plant-based chitosan is derived from chitin, which is a structural element of the cell walls of fungi (Aspergillus niger). It is a non-toxic raw material, with low allergenicity. It is also biodegradable.
Plant-based chitosan can be used by vegans and vegetarians, as well as people with shellfish allergies.
Chitosan – applications in medicine
Thanks to its biocompatibility, biodegradability and non-toxic nature, chitosan, also exhibits anti-hemorrhagic, antimicrobial and wound healing properties. It is used in bandages designed to:
- reduce bleeding,
- treat traumatic wounds,
- treat bedsores and chronic ulcers.
Chitosan products can come in powder, nonwoven fabric, sponge or gel form, and can be used as both dressings and artificial skin. Chitosan owes its therapeutic uses primarily to the cationic nature of the compound and its hydrophilicity. It stimulates macrophages and neutrophils that fight pathogens in our body, and additionally stimulates cell activity (including fibroblasts responsible for the production of collagen and elastin), production of cytokines, as well as promotes the processes of angiogenesis. Thus chitosan supports wound healing, stimulates the formation of granulation tissue and reduces scar formation.
Chitosan for weight loss
However, chitosan is not only used in wound dressings and bandages, but also as an ingredient in products taken orally. Thanks to the absorption properties it exhibits in the gastrointestinal tract, it reduces the absorption of fats consumed with food. Based on this mechanism of action, chitosan seems to contribute to improving BMI, the lipid profile and cardiovascular health. Animal studies further indicate a possible antidiabetic effect – studies in rats showed a reduction in blood glucose levels, as well as an effect that reduced tissue insulin resistance. Dietary supplements with chitosan are therefore used both as weight loss aids and taken in the prevention of civilizational diseases, such as obesity, hypertension and diabetes.
Literature:
- https://materialyinzynierskie.pl/chitozan/
- Mazurek P, Kuliński S, Gosk J. Możliwości wykorzystania chityny i chitozanu w leczeniu ran. Polim. Med. 2013, 43(4), 297–302.
- Jonczyk P, Kandefer B, Potempa M i wsp. Chitosan a gospodarka węglowodanowo-lipidowa. Forum Zaburzeń Metabolicznych 2016, 7(1), 31-34.
- Cheung RCF, Ng TB, Wong JH, Chan WY. Chitosan: An Update on Potential Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13(8), 5156-5186.


